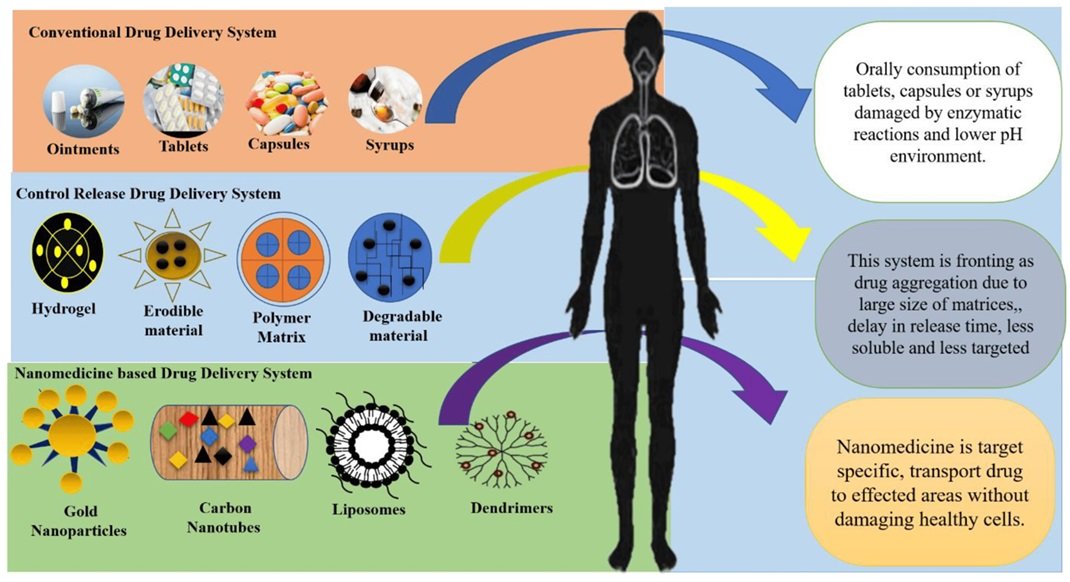
In the realm of modern medicine, the utilization of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery has emerged as a groundbreaking approach to enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. This article delves into the innovative designs of nanoparticles for drug delivery, exploring their definition, applications in targeted therapy, and advancements in non-invasive drug delivery techniques.
Definition of Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles are minute structures, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers in size, engineered to carry therapeutic agents to specific sites within the body. Composed of various materials such as metals, polymers, or lipids, nanoparticles exhibit unique properties due to their small size and large surface area-to-volume ratio. These properties make them ideal candidates for targeted drug delivery. In essence, what is nanoparticles can be summarized as highly specialized carriers designed to transport drugs precisely to diseased tissues while minimizing exposure to healthy cells.
Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery
One of the most significant advancements in drug delivery is the development of nanoparticles tailored for targeted therapy. These nanoparticles can be functionalized with ligands or antibodies that recognize specific cell surface receptors or biomarkers associated with disease. By exploiting these targeting mechanisms, nanoparticles can selectively bind to diseased cells, delivering therapeutic agents directly to the site of action while minimizing systemic exposure and off-target effects.
Innovative Designs of Nanoparticles
Recent innovations in nanoparticle design have focused on enhancing their stability, biocompatibility, and drug-loading capacity. Multifunctional nanoparticles, incorporating imaging agents or stimuli-responsive components, enable real-time monitoring of drug release and therapeutic efficacy. Additionally, the development of nanoparticle-based platforms, such as liposomes, polymeric micelles, and dendrimers, offers versatile delivery systems capable of encapsulating a wide range of drugs and bioactive molecules.
Non-Invasive Drug Delivery Techniques
Innovative nanoparticle designs have also facilitated the development of non-invasive drug delivery techniques, allowing for targeted therapy without the need for invasive procedures. Techniques such as transdermal nanoparticle delivery and inhalation-based nanoparticle formulations offer convenient and patient-friendly alternatives to traditional routes of administration. These non-invasive approaches enhance patient compliance and facilitate the administration of therapeutics for a wide range of diseases.
Future Perspectives and Challenges
While the potential of nanoparticles for drug delivery is vast, several challenges remain to be addressed. These include optimizing nanoparticle properties for enhanced targeting and biocompatibility, ensuring efficient drug loading and controlled release kinetics, and overcoming barriers to translation from preclinical studies to clinical applications. Additionally, safety concerns regarding nanoparticle toxicity and long-term effects on biological systems require careful evaluation and mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
Innovative nanoparticle designs hold tremendous promise for revolutionizing drug delivery and advancing personalized medicine. By harnessing the unique properties of nanoparticles, researchers can develop targeted therapies with enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects. As advancements in nanotechnology continue to unfold, the future of drug delivery looks increasingly promising, paving the way for more effective treatments and improved patient outcomes.
Read More: Muscle Recovery with Remedial Massage: How It Works